What is Forex?
Foreign exchange, commonly known as Forex (FX), is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. As a decentralized global market, it enables banks, financial institutions, investors, and individuals to trade currencies around the clock, with an average daily trading volume exceeding $5 trillion. Unlike most financial markets, the Forex market has no physical exchange or centralized location. Instead, it operates 24 hours a day, five days a week.
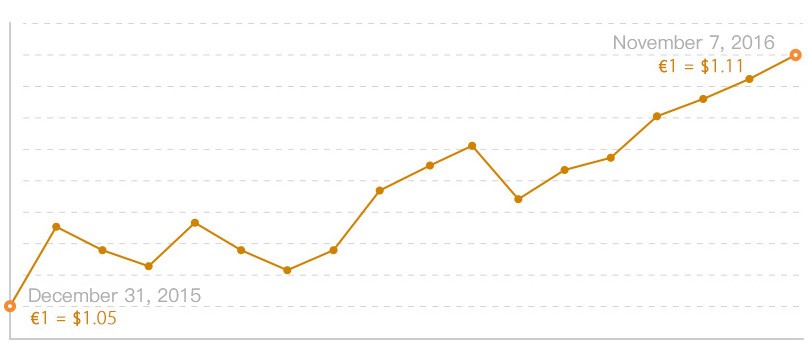
An exchange rate is the price at which one currency is converted into another, representing its value relative to another currency. Since currencies vary in name and value across countries, exchange rates determine the conversion ratio between them. For example, on December 31, 2015, one euro (EUR) was worth approximately $1.05. By November 7, 2016, the exchange rate had risen to $1.11 per euro, reflecting a 5.7% appreciation of the euro against the U.S. dollar (USD) during that period. Some currencies have fixed exchange rates, such as the Hong Kong Dollar (HKD) pegged to the U.S. Dollar (USD). This peg stabilizes the currency but limits its investment potential compared to freely floating currencies.
 XAUUSD chart on TradingView
XAUUSD chart on TradingView
Forex trading involves simultaneously buying one currency while selling another in the foreign exchange market. For example, suppose the U.S. dollar (USD) is expected to weaken relative to the euro (EUR). In this case, a forex trader would sell USD and buy EUR. If the euro strengthens, the trader can then sell EUR to buy back more USD, profiting from the exchange rate difference. This process is similar to stock trading, where traders buy stocks expecting their price to rise and sell them later for a profit. However, the key difference in forex trading is that traders can easily profit in both rising and falling markets. In addition to buying, traders can also sell short, making forex trading highly flexible.
Exchange rates are influenced by various factors, including political and economic stability, monetary policy, central bank interventions, and natural disasters (such as earthquakes and tsunamis). These elements make forex trading highly dynamic and attractive to investors. Due to the high liquidity of the forex market, prices can change rapidly, and a currency’s value fluctuates based on supply and demand dynamics:
• Increased supply or decreased demand for a currency can cause its value to fall.
• Decreased supply or increased demand for a currency can cause its value to rise.
Forex traders can trade in any corner of the world, 24 hours a day, 5 days a week.
Double opportunities from two-way trading (Up and Down)In forex trading, there is no distinction between bull and bear markets. Traders can profit in both rising and falling markets. In addition to "buying low and selling high," traders can sell a currency when they expect its exchange rate to decline and buy it back at a lower rate. As long as the right trading decisions are made, profits can be realized regardless of market direction.
Low trading costMost forex brokers do not charge commissions but instead profit from the bid-ask spread (the difference between the bid and ask prices). At CF Global Trade, our spreads are among the most competitive in the industry. Click here to see details.
Leverage up to 1:500Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller capital outlay, improving capital efficiency. Leverage ratios vary by product, with the maximum leverage for margin-based forex trading reaching 1:500. This means that with $1,000 in their account, a trader can control a position worth $500,000. However, it is essential to implement effective risk management, as high leverage can amplify both profits and losses.
Decentralized, Transparent, and FairForex traders include governments, banks, institutions, and individual investors worldwide. With an average daily trading volume exceeding $5 trillion, the sheer size of the forex market makes it impossible for any single country or entity to manipulate at will. Additionally, forex market trends and exchange rates fluctuate due to global events, economic shifts, and policy changes. As a result, the forex market operates in a decentralized and fair manner, leaving no room for manipulation or behind-the-scenes interference.
Initial Margin refers to the amount of money a trader must deposit to open a position in the market.
Day Trade Margin and Weekend Margin• Day Trade Margin is the margin requirement a trader must maintain during trading hours. If the requirement is not met, the trader must close or offset the position.
• Weekend Margin refers to the margin requirement for holding positions overnight. If the required margin is not maintained, the position must be closed before the market session ends.
SpreadA spread refers to the difference between the bid and ask prices. For traders, a smaller spread results in lower trading costs.
Over the long run, spreads can significantly impact the overall profits or losses of day traders but have minimal effect on mid- and long-term traders.
In forex trading, there are two key prices: the buy price, known as the 'BID,' and the sell price, known as the 'ASK.' The spread refers to the difference between these two prices.
Profit & Loss Calculation Formula:
Gross profit or loss=(ASK − BID) × contract unit × traded lots+overnight interest (if any) − commission (if any)
If you trade 0.5 lots of EUR/USD through the CF Global Trade Platform, where 1 lot equals €100,000, the BID price is 1.1050, and the ASK price at closing one the same day is 1.1090,
the gross profit is calculated as follows:
Gross profit or loss = (ASK−BID) × contract unit × traded lots+overnight interest − commission
(1.1090 − 1.1050) × 100,000 × 0.5 = $200
Total gross profit: $200.
If you trade 1 lot of EUR/USD through the CF Global Trade Platform, where 1 lot equals €100,000, the ASK price at opening is 1.1100, and the BID price at closing on the same day is 1.1030,
the gross profit is calculated as follows:
Gross profit or loss=(ASK − BID) × contract unit × traded lots+overnight interest − commission
(1.1100 − 1.1030) × 100,000 × 1=$700
Total gross profit:$700
-
 Terms of Forex Contract
Terms of Forex ContractProvide 20 major currency pairs worldwide, low spreads, and leverage up to about 1:500
-
 Learn about CF Global Trade platform
Learn about CF Global Trade platformThere are a total of 68 kinds of CF Global Trade trading platforms for margin trading, which support computer and mobile versions, various charts, and technical indicator analysis.
Join us
Different trading models share the same investment opportunity. Open an account anytime and download the platform